| Location: Home > Research > Research Progress |
| Ontogenetic Studies Indicating the Sternum Formed Differently in Enantiornithines and Ornithuromorphs |
|
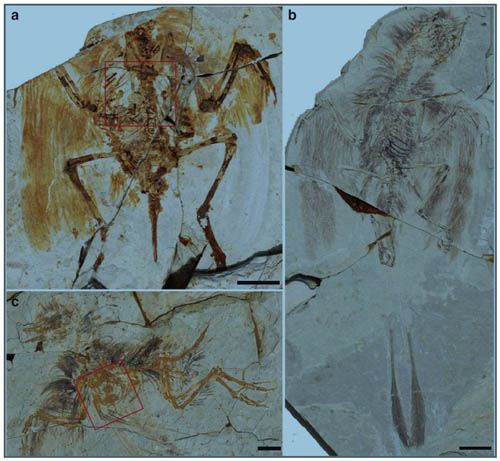
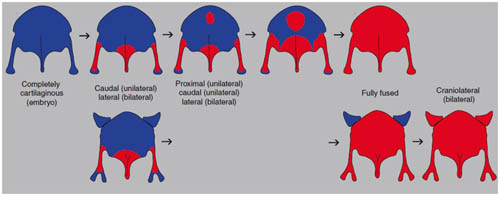
In an article online October 9 in Nature Communications, postdoctoral researcher Jingmai O'Connor and Zhou Zhonghe, director of the CAS Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology (IVPP) collaborated with Zheng Xiaoting and Wang Xiaoli from Shandong’s Linyi University, reveal for the first time the formation of the sternum in the largest group of Cretaceous birds, Enantiornithes, highlighting the importance of ontogenetic studies for understanding homology and the evolution of skeletal features in palaeontology. The study is based on information from new juvenile specimens from the Shandong Tianyu Museum of Nature; these discoveries reveal rare ontogenetic information, in this case the ossification of the sternum, one of the most important elements in the bird skeleton (the two largest and most powerful flight muscles attach to this bone). The study uncovers a major difference between the sternum in Enantiornithes and all other known groups of birds. The enantiornithine sternum forms from four to six ossification centers, three of which are recognized for the first time; the sternal body primarily forms from two non-symmetrical unilateral ossifications, the caudal of which ossifies first. In contrast, living birds ossify the sternal body from a mediolaterally symmetrical pair of sternal ossifications as in other dinosaurs, and ossifications proceeds from the front to the back. A number of similar features (e.g. ventral keel, caudal trabeculae, craniolateral processes) that distinguish the sterna of enantiornithines and ornithuromorphs (the group that includes living birds) from other groups are now revealed to have very different developmental origins; this suggests these features are not fully homologous, highlighting the high degree of homoplasy that characterizes the dinosaur bird transition and the importance of development for testing hypotheses of homology. This study suggests that many of the features that unite Enantiornithes and Ornithuromorpha as sister-groups may represent parallelisms and through a better understanding of development, this relationship may no longer be supported. The research was mainly supported by the 973 Project and the National Natural Science Foundation.
Fig.1: New juvenile specimens assigned to Enantiornithes indet. (Image by Jingmai O'Connor)
Fig.2: Interpretative drawing of the development of the enantiornithine sternum. Red indicates bone and blue indicates cartilage. (Image by Jingmai O'Connor) |