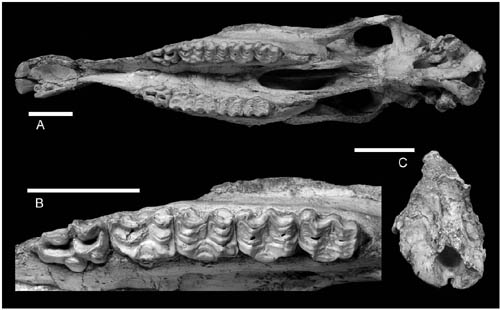
In a study published in the latest issue of of
Vertebrata PalAsiatic 2012(1), Dr. DENG Tao, Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology (IVPP), Chinese Academy of Sciences in Beijing, reported a skull of
Hipparion (
Proboscidipparion)
sinense from the Longdan locality in Dongxiang, Gansu Province, northwestern China. The previously known material of this species in the Early Pleistocene Longdan fauna was only a Metacarpal III. This find not only confirms the specific identification of
Hipparion in this fauna, but also increases the understanding of the cranial and dental characters of this species.
Proboscidipparion is a derived, large- to giant-sized form of the three-toed horse with a special muzzle structure, and its nasal notch reaches deeply above the middle part of the cheek tooth row. Their distribution was limited to northern China, but recent studies expanded its distribution as far as to England.
The new specimen was unearthed from the lower part of the Early Pleistocene Wucheng Loess at Shitougu of Nalesi Town, Dongxiang County, Gansu Province. It is a juvenile male individual with an erupted large-sized canine. Its age is approximately 2.5 years determined by the eruption of its cheek teeth.
The holotype specimen of
Hipparion sinense belongs to a senile individual, and no other complete skull of this species has been found. Therefore, the new material from Longdan provides some key information for the diagnoses of
Hipparion sinense, and reveals the structure of the nasal notch of this species. The lower part of the nasal bone is a tenuous strip that extends far forward, comprises the posterior part of the lower margin of the nasal notch, and has a sharp anterior end reaching the level of the P2/P3 boundary, at a 30 mm distance from the posterior end of the nasal process of the premaxillary bone. “The recognition of these characters is greatly important in determining the phylogenetic relationship of Proboscidipparion”, said Deng Tao.
Proboscidipparion might prefer living in an area with abundant water, same as tapirs which have a similar nasal structure. The discovery of
Proboscidipparion at Longdan further supports the environmental implications of fossil beavers and other members of the Longdan fauna, indicating streams and small lakes for the Linxia Basin during the Early Pleistocene.
This work was supported by the National Program on Key Basic Research Project of China, Main Direction Program of Knowledge Innovation of Chinese Academy of Sciences, National Natural Science Foundation of China, and National Committee on Stratigraphy.
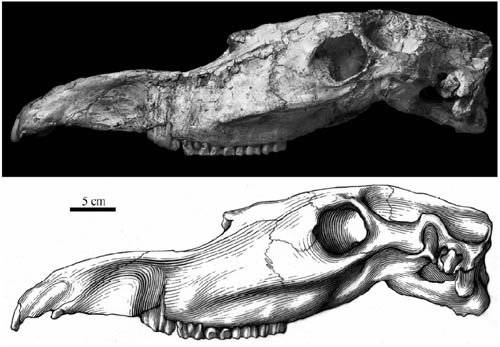
Fig.1 Lateral view of the skull of
Hipparion (Proboscidipparion)
sinense from Longdan (HMV 1872) (Image by DENG Tao)
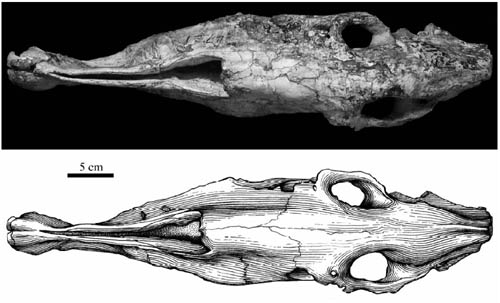
Fig.2 Dorsal view of the skull of
Hipparion (
Proboscidipparion)
sinense from Longdan (HMV 1872) (Image by DENG Tao)